Radios may be required to obtain a license to operate in an area or be part of the FCC approved unlicensed ISM band. Radio technologies in the ISM band are most commonly available supporting either "open" or proprietary standards. It is within the "open" standards such as 802.11 where most security issues are prevalent and primarily what this document will discuss.
Typical 802.11a/b/g (DSSS) wireless LAN architectures consist of wireless clients, wireless access points, wired computers and industrial PLC processors. Wireless Clients typically are laptop computers but can also be industrial protocol/network gateways or PLC rack based modules. These wireless clients can communicate to other "wired" devices over LANs typically through a wireless access point (AP) in "Infrastructure" mode or communicate directly with each other peer-to-peer in "Ad hoc" mode. An access point provides coverage to a particular area known as a cell or "Hot-Spot" and is usually connected to the wired network.
Some access points like the ProSoft Technology RLX-IH act as a repeater and allow for a "wireless" backbone connecting several wireless hotspots
The goal of wireless network implementations is to provide benefits identical to common wired networks and protect the network and resources from security related issues. Protecting the wired or wireless network may require a sequence of events to occur depending on whether the resources are part of the corporate LAN and/or industrial networks:
- Authentication is the verification process by which a user attempts to confirm identification with network resources to establish trust with the available resources.
- Authorization protects computer resources by only allowing those resources to be used by resource consumers that have been granted authority to use them. Provides
- Encryption is the process of obscuring information to make it unreadable without special knowledge.
- Integrity refers to the validity of data from malicious and accidental altering.
Authentication: Open and Shared
- Open system authentication: This is the default setting where any client can associate with the access point.
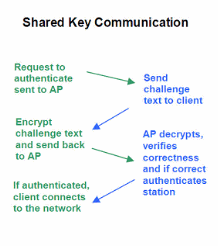
- Shared key authentication: Uses a shared secret key to authenticate the client to the AP. Uses a challenge-response protocol
Authorization: MAC Layer
- Can configure the AP to talk to specific MAC addresses
- Controls access to wired network not wireless
A network missing any of these elements may expose known vulnerabilities to hackers and allow them to breach the confidentiality and integrity of the network resources.
The need for wireless security is obvious but what are the top most security areas of concern and are these security concerns really related to all wireless network applications - Corporate and Industrial ?
What are the top seven wireless security problems confronting corporate LANs and industrial automation applications?
Seven Security Problems of 802.11
- 1 Easy Access
- 2 Rogue Access points
- 3 Unauthorized use of service
- 4 Service and performance constraints
- 5 MAC spoofing and Session Hijacking
- 6 Traffic Analysis and Eavesdropping
- 7 Higher Level Attacks
Each of these concerns can be grouped into two specific areas.
Area A- Security concerns relating to issues when accessing corporate LANS through authentication and authorization and
Area B - Security concerns relating to issues about over-the-air wireless data packets.
Many industrial wireless applications are not subject to all of these security issues because not all wireless devices require connection to the corporate/industrial LAN and need only to be concerned with Area B security concerns. Grouping of these security concerns helps wireless site planners focus their attention to specific areas of security.
Each of the above seven concerns are grouped and defined below with suggestions to help guide the planner to avoid getting into trouble when setting up a wireless network.